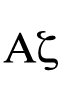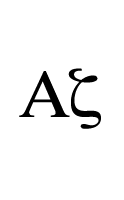shared views are OK,
but there are differences, that is the real challenge and there is no easy way,
it is not a matter of understanding but creative production of new meanings,
..some thoughts from S.Zizek:
Then let's return to some of the things that have been surprising us. In a recent article, you made the point that the terrorists mirror our civilisation. They are not out there, but mirror our own Western world. Can you elaborate on that some more?
Slavoj Zizek:
This, of course, is my answer to this popular thesis by Samuel P Huntington and others that there is a so-called clash of civilisations. I don't buy this thesis, for a number of reasons.
Today's racism is precisely this racism of cultural difference. It no longer says: 'I am more than you.' It says: 'I want my culture, you can have yours.' Today, every right-winger says just that. These people can be very postmodern. They acknowledge that there is no natural tradition, that every culture is artificially constructed. In France, for example, you have a neo-fascist right that refers to the deconstructionists, saying: 'Yes, the lesson of deconstructionism against universalism is that there are only particular identities. So, if blacks can have their culture, why should we not have ours?'
We should also consider the first reaction of the American 'moral majority', specifically Jerry Falwell and Pat Robertson, to the 11 September attacks. Pat Robertson is a bit eccentric, but Jerry Falwell is a mainstream figure, who endorsed Reagan and is part of the mainstream, not an eccentric freak. Now, their reaction was the same as the Arabs', though he did retract a couple of days later. Falwell said the World Trade Centre bombings were a sign that God no longer protects the USA, because the USA had chosen a path of evil, homosexuality and promiscuity.
According to the FBI, there are now at least two million so-called radical right-wingers in the USA. Some are quite violent, killing abortion doctors, not to mention the Oklahoma City bombing. To me, this shows that the same anti-liberal, violent attitude also grows in our own civilisation. I see that as proof that this terrorism is an aspect of our time. We cannot link it to a particular civilisation.
Regarding Islam, we should look at history. In fact, I think it is very interesting in this regard to look at ex-Yugoslavia. Why was Sarajevo and Bosnia the place of violent conflict? Because it was ethnically the most mixed republic of ex-Yugoslavia. Why? Because it was Muslim-dominated, and historically they were definitely the most tolerant. We Slovenes, on the other hand, and the Croats, both Catholics, threw them out several hundred years ago.
This proves that there is nothing inherently intolerant about Islam. We must rather ask why this terrorist aspect of Islam arises now. The tension between tolerance and fundamentalist violence is within a civilisation.
Take another example: on CNN we saw President Bush present a letter of a seven-year-old girl whose father is a pilot and now around Afghanistan. In the letter she said that she loves her father, but if her country needs his death, she is ready to give her father for her country. President Bush described this as American patriotism. Now, do a simple mental experiment - imagine the same event with an Afghan girl saying that. We would immediately say: 'What cynicism, what fundamentalism, what manipulation of small children.' So there is already something in our perception. But what shocks us in others we ourselves also do in a way.
So multiculturalism and fundamentalism could be two sides of the same coin?
Slavoj Zizek:
There is nothing to be said against tolerance. But when you buy this multiculturalist tolerance, you buy many other things with it. Isn't it symptomatic that multiculturalism exploded at the very historic moment when the last traces of working-class politics disappeared from political space? For many former leftists, this multiculturalism is a kind of ersatz working-class politics. We don't even know whether the working class still exists, so let's talk about exploitation of others.
There may be nothing wrong with that as such. But there is a danger that issues of economic exploitation are converted into problems of cultural tolerance. And then you have only to make one step further, that of Julia Kristeva in her essay 'Etrangers à nous mêmes', and say we cannot tolerate others because we cannot tolerate otherness in ourselves. Here we have a pure pseudo-psychoanalytic cultural reductionism.
Isn't it sad and tragic that the only relatively strong - not fringe - political movement that still directly addresses the working class is made up of right-wing populists? They are the only ones. Jean-Marie Le Pen in France, for example. I was shocked when I saw him three years ago at a congress of the Front National. He brought a black Frenchman, an Algerian and a Jew on the podium, embraced them and said: 'They are no less French than I am. Only the international cosmopolitan companies who neglect French patriotic interests are my enemy.' So the price is that only right-wingers still talk about economic exploitation.
The second thing I find wrong with this multiculturalist tolerance is that it is often hypocritical in the sense that the other whom they tolerate is already a reduced other. The other is okay in so far as this other is only a question of food, of culture, of dances. What about clitoridectomy? What about my friends who say: 'We must respect Hindus.' Okay, but what about one of the old Hindu customs which, as we know, is that when a husband dies, the wife is burned. Now, do we respect that? Problems arise here.
An even more important problem is that this notion of tolerance effectively masks its opposite: intolerance. It is a recurring theme in all my books that, from this liberal perspective, the basic perception of another human being is always as something that may in some way hurt you.
Are you referring to what we call victim culture?
Slavoj Zizek:
The discourse of victimisation is almost the predominant discourse today. You can be a victim of the environment, of smoking, of sexual harassment. I find this reduction of the subject to a victim sad. In what sense? There is an extremely narcissistic notion of personality here. And, indeed, an intolerant one, insofar as what it means is that we can no longer tolerate violent encounters with others - and these encounters are always violent.
Let me briefly address sexual harassment for a moment. Of course I am opposed to it, but let's be frank. Say I am passionately attached, in love, or whatever, to another human being and I declare my love, my passion for him or her. There is always something shocking, violent in it. This may sound like a joke, but it isn't - you cannot do the game of erotic seduction in politically correct terms. There is a moment of violence, when you say: 'I love you, I want you.' In no way can you bypass this violent aspect. So I even think that the fear of sexual harassment in a way includes this aspect, a fear of a too violent, too open encounter with another human being.
Another thing that bothers me about this multiculturalism is when people ask me: 'How can you be sure that you are not a racist?' My answer is that there is only one way. If I can exchange insults, brutal jokes, dirty jokes, with a member of a different race and we both know it's not meant in a racist way. If, on the other hand, we play this politically correct game - 'Oh, I respect you, how interesting your customs are' - this is inverted racism, and it is disgusting.
In the Yugoslav army where we were all of mixed nationalities, how did I become friends with Albanians? When we started to exchange obscenities, sexual innuendo, jokes. This is why this politically correct respect is just, as Freud put it, 'zielgehemmt'. You still have the aggression towards the other.
For me there is one measure of true love: you can insult the other. Like in that horrible German comedy film from 1943 where Marika Röck treats her fiancé very brutally. This fiancé is a rich, important person, so her father asks her why are you treating him like that. And she gives the right answer. She says: 'But I love him, and since I love him, I can do with him whatever I want.' That's the truth of it. If there is true love, you can say horrible things and anything goes.
When multiculturalists tell you to respect the others, I always have this uncanny association that this is dangerously close to how we treat our children: the idea that we should respect them, even when we know that what they believe is not true. We should not destroy their illusions. No, I think that others deserve better - not to be treated like children.
In your book on the subject you talk of a 'true universalism' as an opposite of this false sense of global harmony. What do you mean by that?
Slavoj Zizek:
Here I need to ask myself a simple Habermasian question: how can we ground universality in our experience? Naturally, I don't accept this postmodern game that each of us inhabits his or her particular universe. I believe there is universality. But I don't believe in some a priori universality of fundamental rules or universal notions. The only true universality we have access to is political universality. Which is not solidarity in some abstract idealist sense, but solidarity in struggle.
If we are engaged in the same struggle, if we discover that - and this for me is the authentic moment of solidarity - being feminists and ecologists, or feminists and workers, we all of a sudden have this insight: 'My God, but our struggle is ultimately the same!' This political universality would be the only authentic universality. And this, of course, is what is missing today, because politics today is increasingly a politics of merely negotiating compromises between different positions.
The post-political subverts the freedom that has been talked about so much in recent weeks. Is that what you are saying?
Slavoj Zizek:
I do claim that what is sold to us today as freedom is something from which this more radical dimension of freedom and democracy has been removed - in other words, the belief that basic decisions about social development are discussed or brought about involving as many as possible, a majority. In this sense, we do not have an actual experience of freedom today. Our freedoms are increasingly reduced to the freedom to choose your lifestyle. You can even choose your ethnic identity up to a point.
But this new world of freedom described by people like Ulrich Beck, who say everything is a matter of reflective negotiation, of choice, can include new unfreedom. My favourite example is this, and here we have ideology at its purest: we know that it is very difficult today in more and more professional domains to get a long-term job. Academics or journalists, for example, now often live on a two- or three-year contract, that you then have to renegotiate. Of course, most of us experience this as something traumatising, shocking, where you can never be sure. But then, along comes the postmodern ideologist: 'Oh, but this is just a new freedom, you can reinvent yourself every two years!'
The problem for me is how unfreedom is hidden, concealed in precisely what is presented to us as new freedoms. I think that the explosion of these new freedoms, which fall under the domain of what Michel Foucault called 'care of the self', involves greater social unfreedom.
Twenty or 30 years ago there was still discussion as to whether the future would be fascist, socialist, communist or capitalist. Today, nobody even discusses this. These fundamental social choices are simply no longer perceived as a matter to decide. A certain domain of radical social questions has simply been depoliticised.
I find it very sad that, precisely in an era in which tremendous changes are taking place and, indeed entire social coordinates are transformed, we don't experience this as something about which we decided freely.
So, let's return to the aftermath of 11 September. We now experience a strange kind of war that we are told will not end for a long time. What do you think of this turn of events?
Slavoj Zizek:
I don't quite agree with those who claim that this World Trade Centre explosion was the start of the first war of the twenty-first century. I think it was a war of the twentieth century, in the sense that it was still a singular, spectacular event. The new wars would be precisely as you mentioned - it will not even be clear whether it is a war or not. Somehow life will go on and we will learn that we are at war, as we are now.
What worries me is how many Americans perceived these bombings as something that made them into innocents: as if to say, until now, we had problems, Vietnam, and so on. Now we are victims, and this somehow justifies us in fully identifying with American patriotism.
That's a risky gesture. The big choice for Americans is whether they retreat into this patriotism - or, as my friend Ariel Dorfman wrote recently: 'America has the chance to become a member of the community of nations. America always behaves as though it were special. It should use this attack as an opportunity to admit that it is not special, but simply and truly part of this world.' That's the big choice.
There is something so disturbingly tragic in this idea of the wealthiest country in the world bombing one of the poorest countries. It reminds me of the well-known joke about the idiot who loses a key in the dark and looks for it beneath the light. When asked why, he says: 'I know I lost it over there, but it's easier to look for it here.'
But at the same time I must confess that the left also deeply disappointed me. Falling back into this safe pacifist attitude - violence never stops violence, give peace a chance - is abstract and doesn't work here. First, because this is not a universal rule. I always ask my leftist friends who repeat that mantra: What would you have said in 1941 with Hitler. Would you also say: 'We shouldn't resist, because violence never helps?' It is simply a fact that at some point you have to fight. You have to return violence with violence. The problem is not that for me, but that this war can never be a solution.
It is also false and misleading to perceive these bombings as some kind of third world working-class response to American imperialism. In that case, the American fundamentalists we already discussed, are also a working-class response, which they clearly are not. We face a challenge to rethink our coordinates and I hope that this will be a good result of this tragic event. That we will not just use it to do more of the same but to think about what is really changing in our world.
From: Spiked 15 November 2001.
Available: http://www.spiked-online.com/Articles/00000002D2C4.htm
----- Original Message ----- From: "Cheryl McGrath" <csmcgrath@xxxxxxxxxxxxx>
To: "open discussion" <design-l.v2@xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx>
Sent: Wednesday, July 13, 2005 5:23 PM
Subject: Re: [design] the world view (3)
but there are differences, that is the real challenge and there is no easy way,
it is not a matter of understanding but creative production of new meanings,
..some thoughts from S.Zizek:
Then let's return to some of the things that have been surprising us. In a recent article, you made the point that the terrorists mirror our civilisation. They are not out there, but mirror our own Western world. Can you elaborate on that some more?
Slavoj Zizek:
This, of course, is my answer to this popular thesis by Samuel P Huntington and others that there is a so-called clash of civilisations. I don't buy this thesis, for a number of reasons.
Today's racism is precisely this racism of cultural difference. It no longer says: 'I am more than you.' It says: 'I want my culture, you can have yours.' Today, every right-winger says just that. These people can be very postmodern. They acknowledge that there is no natural tradition, that every culture is artificially constructed. In France, for example, you have a neo-fascist right that refers to the deconstructionists, saying: 'Yes, the lesson of deconstructionism against universalism is that there are only particular identities. So, if blacks can have their culture, why should we not have ours?'
We should also consider the first reaction of the American 'moral majority', specifically Jerry Falwell and Pat Robertson, to the 11 September attacks. Pat Robertson is a bit eccentric, but Jerry Falwell is a mainstream figure, who endorsed Reagan and is part of the mainstream, not an eccentric freak. Now, their reaction was the same as the Arabs', though he did retract a couple of days later. Falwell said the World Trade Centre bombings were a sign that God no longer protects the USA, because the USA had chosen a path of evil, homosexuality and promiscuity.
According to the FBI, there are now at least two million so-called radical right-wingers in the USA. Some are quite violent, killing abortion doctors, not to mention the Oklahoma City bombing. To me, this shows that the same anti-liberal, violent attitude also grows in our own civilisation. I see that as proof that this terrorism is an aspect of our time. We cannot link it to a particular civilisation.
Regarding Islam, we should look at history. In fact, I think it is very interesting in this regard to look at ex-Yugoslavia. Why was Sarajevo and Bosnia the place of violent conflict? Because it was ethnically the most mixed republic of ex-Yugoslavia. Why? Because it was Muslim-dominated, and historically they were definitely the most tolerant. We Slovenes, on the other hand, and the Croats, both Catholics, threw them out several hundred years ago.
This proves that there is nothing inherently intolerant about Islam. We must rather ask why this terrorist aspect of Islam arises now. The tension between tolerance and fundamentalist violence is within a civilisation.
Take another example: on CNN we saw President Bush present a letter of a seven-year-old girl whose father is a pilot and now around Afghanistan. In the letter she said that she loves her father, but if her country needs his death, she is ready to give her father for her country. President Bush described this as American patriotism. Now, do a simple mental experiment - imagine the same event with an Afghan girl saying that. We would immediately say: 'What cynicism, what fundamentalism, what manipulation of small children.' So there is already something in our perception. But what shocks us in others we ourselves also do in a way.
So multiculturalism and fundamentalism could be two sides of the same coin?
Slavoj Zizek:
There is nothing to be said against tolerance. But when you buy this multiculturalist tolerance, you buy many other things with it. Isn't it symptomatic that multiculturalism exploded at the very historic moment when the last traces of working-class politics disappeared from political space? For many former leftists, this multiculturalism is a kind of ersatz working-class politics. We don't even know whether the working class still exists, so let's talk about exploitation of others.
There may be nothing wrong with that as such. But there is a danger that issues of economic exploitation are converted into problems of cultural tolerance. And then you have only to make one step further, that of Julia Kristeva in her essay 'Etrangers à nous mêmes', and say we cannot tolerate others because we cannot tolerate otherness in ourselves. Here we have a pure pseudo-psychoanalytic cultural reductionism.
Isn't it sad and tragic that the only relatively strong - not fringe - political movement that still directly addresses the working class is made up of right-wing populists? They are the only ones. Jean-Marie Le Pen in France, for example. I was shocked when I saw him three years ago at a congress of the Front National. He brought a black Frenchman, an Algerian and a Jew on the podium, embraced them and said: 'They are no less French than I am. Only the international cosmopolitan companies who neglect French patriotic interests are my enemy.' So the price is that only right-wingers still talk about economic exploitation.
The second thing I find wrong with this multiculturalist tolerance is that it is often hypocritical in the sense that the other whom they tolerate is already a reduced other. The other is okay in so far as this other is only a question of food, of culture, of dances. What about clitoridectomy? What about my friends who say: 'We must respect Hindus.' Okay, but what about one of the old Hindu customs which, as we know, is that when a husband dies, the wife is burned. Now, do we respect that? Problems arise here.
An even more important problem is that this notion of tolerance effectively masks its opposite: intolerance. It is a recurring theme in all my books that, from this liberal perspective, the basic perception of another human being is always as something that may in some way hurt you.
Are you referring to what we call victim culture?
Slavoj Zizek:
The discourse of victimisation is almost the predominant discourse today. You can be a victim of the environment, of smoking, of sexual harassment. I find this reduction of the subject to a victim sad. In what sense? There is an extremely narcissistic notion of personality here. And, indeed, an intolerant one, insofar as what it means is that we can no longer tolerate violent encounters with others - and these encounters are always violent.
Let me briefly address sexual harassment for a moment. Of course I am opposed to it, but let's be frank. Say I am passionately attached, in love, or whatever, to another human being and I declare my love, my passion for him or her. There is always something shocking, violent in it. This may sound like a joke, but it isn't - you cannot do the game of erotic seduction in politically correct terms. There is a moment of violence, when you say: 'I love you, I want you.' In no way can you bypass this violent aspect. So I even think that the fear of sexual harassment in a way includes this aspect, a fear of a too violent, too open encounter with another human being.
Another thing that bothers me about this multiculturalism is when people ask me: 'How can you be sure that you are not a racist?' My answer is that there is only one way. If I can exchange insults, brutal jokes, dirty jokes, with a member of a different race and we both know it's not meant in a racist way. If, on the other hand, we play this politically correct game - 'Oh, I respect you, how interesting your customs are' - this is inverted racism, and it is disgusting.
In the Yugoslav army where we were all of mixed nationalities, how did I become friends with Albanians? When we started to exchange obscenities, sexual innuendo, jokes. This is why this politically correct respect is just, as Freud put it, 'zielgehemmt'. You still have the aggression towards the other.
For me there is one measure of true love: you can insult the other. Like in that horrible German comedy film from 1943 where Marika Röck treats her fiancé very brutally. This fiancé is a rich, important person, so her father asks her why are you treating him like that. And she gives the right answer. She says: 'But I love him, and since I love him, I can do with him whatever I want.' That's the truth of it. If there is true love, you can say horrible things and anything goes.
When multiculturalists tell you to respect the others, I always have this uncanny association that this is dangerously close to how we treat our children: the idea that we should respect them, even when we know that what they believe is not true. We should not destroy their illusions. No, I think that others deserve better - not to be treated like children.
In your book on the subject you talk of a 'true universalism' as an opposite of this false sense of global harmony. What do you mean by that?
Slavoj Zizek:
Here I need to ask myself a simple Habermasian question: how can we ground universality in our experience? Naturally, I don't accept this postmodern game that each of us inhabits his or her particular universe. I believe there is universality. But I don't believe in some a priori universality of fundamental rules or universal notions. The only true universality we have access to is political universality. Which is not solidarity in some abstract idealist sense, but solidarity in struggle.
If we are engaged in the same struggle, if we discover that - and this for me is the authentic moment of solidarity - being feminists and ecologists, or feminists and workers, we all of a sudden have this insight: 'My God, but our struggle is ultimately the same!' This political universality would be the only authentic universality. And this, of course, is what is missing today, because politics today is increasingly a politics of merely negotiating compromises between different positions.
The post-political subverts the freedom that has been talked about so much in recent weeks. Is that what you are saying?
Slavoj Zizek:
I do claim that what is sold to us today as freedom is something from which this more radical dimension of freedom and democracy has been removed - in other words, the belief that basic decisions about social development are discussed or brought about involving as many as possible, a majority. In this sense, we do not have an actual experience of freedom today. Our freedoms are increasingly reduced to the freedom to choose your lifestyle. You can even choose your ethnic identity up to a point.
But this new world of freedom described by people like Ulrich Beck, who say everything is a matter of reflective negotiation, of choice, can include new unfreedom. My favourite example is this, and here we have ideology at its purest: we know that it is very difficult today in more and more professional domains to get a long-term job. Academics or journalists, for example, now often live on a two- or three-year contract, that you then have to renegotiate. Of course, most of us experience this as something traumatising, shocking, where you can never be sure. But then, along comes the postmodern ideologist: 'Oh, but this is just a new freedom, you can reinvent yourself every two years!'
The problem for me is how unfreedom is hidden, concealed in precisely what is presented to us as new freedoms. I think that the explosion of these new freedoms, which fall under the domain of what Michel Foucault called 'care of the self', involves greater social unfreedom.
Twenty or 30 years ago there was still discussion as to whether the future would be fascist, socialist, communist or capitalist. Today, nobody even discusses this. These fundamental social choices are simply no longer perceived as a matter to decide. A certain domain of radical social questions has simply been depoliticised.
I find it very sad that, precisely in an era in which tremendous changes are taking place and, indeed entire social coordinates are transformed, we don't experience this as something about which we decided freely.
So, let's return to the aftermath of 11 September. We now experience a strange kind of war that we are told will not end for a long time. What do you think of this turn of events?
Slavoj Zizek:
I don't quite agree with those who claim that this World Trade Centre explosion was the start of the first war of the twenty-first century. I think it was a war of the twentieth century, in the sense that it was still a singular, spectacular event. The new wars would be precisely as you mentioned - it will not even be clear whether it is a war or not. Somehow life will go on and we will learn that we are at war, as we are now.
What worries me is how many Americans perceived these bombings as something that made them into innocents: as if to say, until now, we had problems, Vietnam, and so on. Now we are victims, and this somehow justifies us in fully identifying with American patriotism.
That's a risky gesture. The big choice for Americans is whether they retreat into this patriotism - or, as my friend Ariel Dorfman wrote recently: 'America has the chance to become a member of the community of nations. America always behaves as though it were special. It should use this attack as an opportunity to admit that it is not special, but simply and truly part of this world.' That's the big choice.
There is something so disturbingly tragic in this idea of the wealthiest country in the world bombing one of the poorest countries. It reminds me of the well-known joke about the idiot who loses a key in the dark and looks for it beneath the light. When asked why, he says: 'I know I lost it over there, but it's easier to look for it here.'
But at the same time I must confess that the left also deeply disappointed me. Falling back into this safe pacifist attitude - violence never stops violence, give peace a chance - is abstract and doesn't work here. First, because this is not a universal rule. I always ask my leftist friends who repeat that mantra: What would you have said in 1941 with Hitler. Would you also say: 'We shouldn't resist, because violence never helps?' It is simply a fact that at some point you have to fight. You have to return violence with violence. The problem is not that for me, but that this war can never be a solution.
It is also false and misleading to perceive these bombings as some kind of third world working-class response to American imperialism. In that case, the American fundamentalists we already discussed, are also a working-class response, which they clearly are not. We face a challenge to rethink our coordinates and I hope that this will be a good result of this tragic event. That we will not just use it to do more of the same but to think about what is really changing in our world.
From: Spiked 15 November 2001.
Available: http://www.spiked-online.com/Articles/00000002D2C4.htm
----- Original Message ----- From: "Cheryl McGrath" <csmcgrath@xxxxxxxxxxxxx>
To: "open discussion" <design-l.v2@xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx>
Sent: Wednesday, July 13, 2005 5:23 PM
Subject: Re: [design] the world view (3)
brian writes
a shared view of the world is possible and necessarydoes anyone have an example of some area
to accurately represent the present situations in a
neutral enough context to make the changes necessary
to secure a new peace- can we develop it together?
of cultural science that might possibly fit
into the islamic views? what, to be more
precise, are some of the scientific islamic
views we could possibly approach and
find common public or private cultural acceptance?
cheryl
_______________________________________________
the design-list, version 2.0 ~ open forum, open ideas ~
http://mail.architexturez.net/mailman/listinfo/design-l.v2